

Des projets de recherche sur l’Habitat Intelligent pour la Santé ont menés en collaboration entre les équipes GETALP du laboratoires LIG (anciennement équipe GEOD du laboratoire CLIPS) et AFIRM du laboratoire TIMC-IMAG entre 2000 et 2008. Les financements qui ont permis d’avancer sur ce thème sont les suivants :
- projet IMAG RESIDE-HIS (IMAG 2000-2002) ;
- projet DESDHIS de l’ACI Santé du Ministère de la Recherche (2002-2004). Thèses de Dan Istrate et Gilles Virone ;
- bourse ministère (bourse de doctorat d’Anthony Fleury) (2004-2008). Thèse soutenue en 2008.
Ces projets étant terminés, cette page n’est plus modifiée depuis décembre 2009.
L’équipe GETALP apportait ses compétences pour la reconnaissance des sons et de la parole, l’équipe AFIRM apportait ses compétences sur les capteurs médicaux et l’évaluation auprès des utilisateurs finaux. Il s’agit d’un thème de recherche à long terme qui vise à aider les personnes, en général âgées ou en difficulté seules à domicile.
- Mots Clefs : Habitat Intelligent, Smart Home, détection de mots clefs de détresse, reconnaissance de la parole, reconnaissance des sons de la vie courante, AVQ (activités de la vie quotidienne)
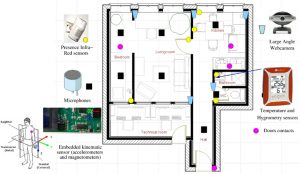
- Appartement HIS de l’équipe AFIRM : plan et vues

- Présentation audiovisuelle du projet
en français (format AVI) ou en anglais (format AVI)
- Participants :
- Michel VACHER (GEOD puis GETALP)
- Jean-François SERIGNAT (ancien responsable de l’équipe GEOD)
- Norbert Noury (responsable de l’équipe AFIRM sur la durée de ces projets)
- Vincent RIALLE (AFIRM)
- Personnes ayant apporté une participation significative à ces projets :
- Stéphane CHAILLOL (GEOD)
- Anthony FLEURY (AFIRM)
- Nicolas GAC (GEOD)
- Hubert GLASSON (GETALP)
- Noë GUIRAND (GETALP)
- Dan ISTRATE (GEOD)
- Pelayo Menendez-Garcia (GEOD)
- François PORTET (GETALP)
- Gilles VIRONE (AFIRM)
Corpus sonore et multimodale
Corpus HIS : corpus enregistré à la fin des projets RESIDE-HIS et DESDHIS (thèse Anthony Fleury) dans l’appartement HIS de l’équipe TIMC-AFIRM, les participants jouent des scénarios comportant des ADL (Activity of Daily Living, ou Activités de la Vie Quotidienne – ADL).
Réalisation
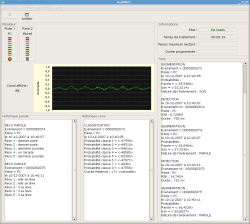 Un logiciel d’analyse sonore a été réalisé et mis en oeuvre dans le HIS (Habitat Intelligent pour la Santé) de l’équipe AFIRM.
Un logiciel d’analyse sonore a été réalisé et mis en oeuvre dans le HIS (Habitat Intelligent pour la Santé) de l’équipe AFIRM.
Caractéristiques principales du logiciel AUDITHIS :
- système d’exploitation Debian/LINUX
- carte d’acquisition multicanal National Instrument
- driver NiDAQmx compatible LINUX
- interruption si 1/2 buffer plein
- 8 voies possibles (microphones)
- 2 applications s’exécutant en parallèle sur un PC unique
- analyse sonore – plusieurs threa
- reconnaissance automatique de la parole (ASR Raphael avec moteur de reconnaissance Janus)
- librairie graphique GTK+
- fonctions et librairies développées en C ou C+
Publications significatives
- [1] A. Fleury, M. Vacher, N. Noury, SVM-Based Multi-Modal Classification of Activities of Daily Living in Health Smart Homes: Sensors, Algorithms and First Experimental Results,
IEEE Transactions on Information Technology in Biomedicine,
vol. 14(2), pp. 274 – 283, 2010. - [2] M. Vacher, F. Portet, A. Fleury, N. Noury, Development of Audio Sensing Technology for Ambient Assisted Living: Applications and Challenges, International Journal of E-Health and Medical Communications (IJEHMC), IGI, 2011, 2 (1), pp.35-54.
- [3] A. Fleury, N. Noury, M. Vacher, H. Glasson and J.-F. Serignat, Sound and Speech Detection and Classification in a Health Smart Home, 30th IEEE EMBS Annual International Conference, “Personalized Healthcare through Technology”, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, Aug20-24, 2008, pp. 4644-4647.Advances in Spoken Language Technology,Iasi, Romania, 10-12 May, 2007, pp. 135-146, ISBN: 978-973-27-1516-1.
- [4] Michel Vacher, Anthony Fleury, Jean-François Serignat, Norbert Noury and Hubert Glasson, Preliminary Evaluation of Speech/Sound Recognition for Telemedicine Application in a Real Environment, INTERSPEECH, Brisbane, Australia, Sep 22-26, 2008, pp. 496-499.
- [5] A. Fleury, M. Vacher, H. Glasson, J.-F. Serignat and N. Noury, Data Fusion in Health Smart Home: Preliminary Individual Evaluation of Two Families of Sensors, ISG 2008, the 6th International Conference of the International Society for Gerontechnology, Pisa, Italy, June 4-7 , 2008, pp. 6p.
- [6] M. Vacher, J.F.Serignat, S. Chaillol, Sound Classification in a Smart Room Environment: an Approach using GMM and HMM Methods, the 4th Conference on Speech Technology and Human-Computer Dialogue, Advances in Spoken Language Technology, Iasi, Romania, 10-12 May, 2007, pp. 135-146, ISBN: 978-973-27-1516-1.
- [7] D. Istrate, M. Vacher, E. Castelli, L. Besacier, J.-F. Serignat, Information Extraction From Sound for Medical Telemonitoring, Information Technology in Biomedicine, IEEE Transactions on, April 2006, vol. 10, issue 2, pp. 264-274, ISSN: 1089-7771.
- [8] M. Vacher, J.-F. Serignat, S. Chaillol, D. Istrate and V. Popescu, Speech and Sound Use in a Remote Monitoring System for Health Care, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Artificial Intelligence, Text Speech and Dialogue, vol. 4188/2006, 2006, pp. 711-718, ISBN: 978-3-540-39090-9.
- [9] M. Vacher, D. Istrate, J.F. Serignat and N. Gac, Detection and Speech/Sound Segmentation in a Smart Room Environment, presented at The 3rd Conference on Speech Technology and Human-Computer Dialogue (Sped 2005), Cluj-Napoca, Romania, May 13-14, 2005, pp. 37-48.
- [10] M. Vacher, D. Istrate and J.F. Serignat, Sound Detection and Classification through Transient Models using Wavelet Coefficient Trees, presented at 12th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO 2004), Vienna, Austria, September 6-10, pp. 1171-1174.